Pregnancy-related deaths remain a pressing concern in the United States, where the maternal mortality rate outpaces that of other high-income countries. Recent studies reveal that over 80 percent of these tragic fatalities are preventable, yet the numbers continue to climb. Between 2018 and 2022, the mortality rate surged, highlighting alarming health disparities among racial and ethnic groups. Factors such as inadequate postpartum care and inconsistent access to healthcare contribute to these preventable deaths. Addressing the rising rates of pregnancy-related deaths necessitates a concerted effort to improve the U.S. healthcare system and ensure equitable care for all expectant and new mothers.
Maternal deaths during childbirth and post-delivery have become a critical issue that demands our attention. The increasing incidence of these fatalities, often rooted in systemic health disparities, underscores the urgent need for enhanced maternal healthcare. Many of these deaths, particularly among marginalized populations, could be avoided with timely medical intervention and resources. The conversation surrounding maternal health must include a reassessment of postpartum care practices and policy reforms that favor equitable access to comprehensive healthcare services. It is essential to foster an environment where every mother receives the quality support needed to ensure safe pregnancies and recoveries.
Understanding the Rise in U.S. Pregnancy-Related Deaths
The United States continues to grapple with a troubling trend in pregnancy-related deaths, with statistics showing that the country has the highest maternal mortality rate among high-income nations. Despite advancements in medical technology and healthcare, the rate of pregnancy-related deaths rose significantly between 2018 and 2022, illustrating a crisis that disproportionately impacts marginalized communities. The alarming data indicates that more than 80 percent of these deaths could have been prevented through effective interventions and comprehensive healthcare policies. This ongoing rise is a reflection of systemic issues within the U.S. healthcare system, making it imperative to address both accessibility and quality of maternal care.
Research has pinpointed several contributing factors to the increased pregnancy-related mortality rate in the U.S. A lack of equitable healthcare access, the existence of maternity care deserts, and implicit biases within medical practices all play a significant role. Furthermore, chronic health conditions among reproductive-age individuals are becoming more prevalent, complicating pregnancies and delivery. Notably, disparities in maternal mortality rates are particularly pronounced among different racial and ethnic groups, with American Indian and Alaska Native women experiencing significantly higher rates of death during pregnancy and childbirth compared to their white and non-Hispanic Black counterparts.
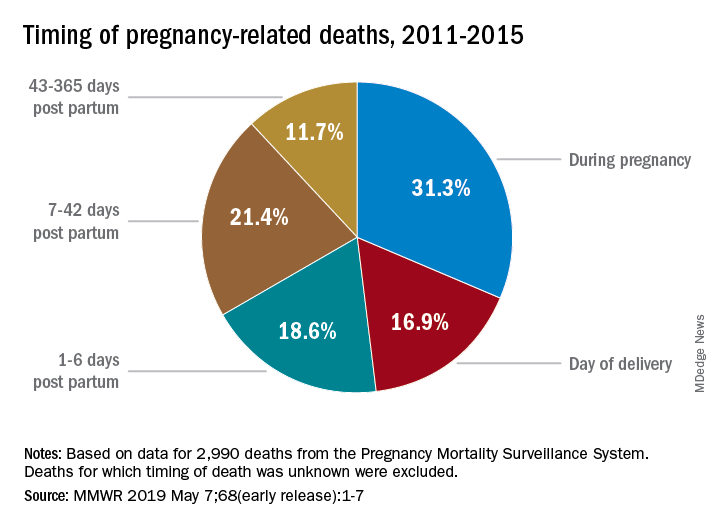
The Importance of Extended Postpartum Care in Reducing Maternal Mortality
Extended postpartum care is crucial in the prevention of pregnancy-related deaths, especially since a considerable percentage of maternal deaths occur after the standard six-week postpartum visit. Many healthcare systems traditionally end postpartum care too soon, neglecting the critical recovery period that extends up to one year post-delivery. Research indicates that these ‘late maternal deaths’ account for nearly a third of all maternal mortality, underscoring the need for a paradigm shift in how healthcare providers think about postpartum care. By fostering a holistic approach that extends care beyond the initial weeks, we can address emerging health issues that can threaten the wellbeing of new mothers.
This shift in focus to extend postpartum care not only improves immediate health outcomes for mothers but also addresses chronic conditions such as hypertension and cardiovascular diseases that could complicate future pregnancies. Encouragingly, innovations and policies aimed at enhancing the quality of postpartum care can lead to better health outcomes, particularly for high-risk groups. Integration of continual health assessment and personalized care plans within the healthcare system can significantly reduce the maternal mortality rate and ensure that women receive the support they need during this vulnerable stage.
Examining Health Disparities in Maternal Mortality Rates
Health disparities continue to be a significant factor contributing to the rising maternal mortality rates in the United States. A new study highlights stark differences in pregnancy-related deaths across various demographics, emphasizing the urgency to address these inequities comprehensively. Among the most affected are American Indian and Alaska Native women, who face pregnancy-related death rates nearly four times higher than white women. This alarming statistic points to long-standing systemic issues—ranging from access to quality healthcare to social determinants of health—that disproportionately affect marginalized populations.
To combat these health disparities, targeted interventions are necessary. Policymakers and healthcare providers must prioritize equitable access to comprehensive maternal healthcare services, especially in regions with known care shortages. By adopting community-focused strategies and creating policies aimed at reducing disparities, the health outcomes for all pregnant individuals can be improved. Ultimately, addressing these disparities requires a multifaceted approach involving public health initiatives, community outreach, and improved data tracking to ensure that every woman has access to the care she needs during pregnancy and beyond.
Preventable Deaths Among Pregnant Women: A Call to Action
The sobering reality that more than 80 percent of pregnancy-related deaths are deemed preventable calls for urgent action from both policymakers and healthcare systems. The findings indicate that systemic changes are necessary to enhance maternal care, including expanded access to screenings for chronic conditions, better prenatal education, and increased investment in maternal health infrastructure. A concerted effort to improve clinical practices and eliminate biases in maternal care can significantly reduce preventable deaths and ensure safer pregnancies for women across the country.
As the U.S. continues to lead high-income nations in maternal mortality rates, innovative solutions are needed to transform the current healthcare landscape. Encouraging states to adopt successful models, like California, which has implemented policies resulting in lower maternal mortality, may pave the way for other states to follow suit. Collaborative efforts across various sectors can lead to a more equitable healthcare system that prioritizes the wellness of mothers and babies alike, ultimately reducing the number of preventable deaths and promoting healthier outcomes for future generations.
The Role of Cardiovascular Disease in Maternal Mortality
Cardiovascular disease has emerged as a leading cause of pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S., accounting for more than 20 percent of cases. This shift in mortality pattern, from causes such as hemorrhage to chronic health issues like hypertension and heart disease, reflects changing health profiles among pregnant individuals. Increased incidences of chronic disease at younger ages suggest a need for heightened awareness and proactive management of maternal health prior to and during pregnancy. Addressing these underlying health conditions is critical to reducing the maternal mortality rate.
Preventive strategies must include routine screenings and education about the risks associated with cardiovascular issues within reproductive-age populations. Medical professionals should be trained to recognize and manage these chronic conditions in pregnant individuals, ensuring that they receive the necessary care throughout their pregnancy. A comprehensive strategy that emphasizes cardiovascular health may not only help reduce pregnancy-related deaths but also improve overall maternal health outcomes.
The Impact of Healthcare Accessibility on Maternal Health
Access to quality healthcare is a fundamental determinant of maternal health outcomes. Unfortunately, the U.S. healthcare system is characterized by significant disparities, particularly evident in rural areas where maternity care services are often limited or non-existent. These maternity care deserts create gaps in access that can prevent pregnant individuals from receiving timely and adequate prenatal care, contributing to higher pregnancy-related mortality rates. To combat this issue, it is essential to develop policies that enhance healthcare access in underserved areas, thereby ensuring that all women receive the necessary resources and support throughout their pregnancies.
Moreover, addressing healthcare accessibility demands a focus on insurance coverage and affordability. Many pregnant individuals, especially those from marginalized backgrounds, may find it challenging to secure adequate insurance that covers comprehensive prenatal and postpartum care. Expanding Medicaid and subsidizing healthcare costs can alleviate these barriers, providing vital support for those most in need. By improving healthcare accessibility, we can significantly contribute to the reduction of preventable pregnancy-related deaths and promote healthier maternal outcomes.
Investing in Public Health Infrastructure for Maternal Health
To reverse the trend of rising maternal mortality rates, investing in public health infrastructure is crucial. Research shows that significant improvements in maternal health outcomes can be achieved through enhanced data collection and tracking systems that accurately report pregnancy-related deaths. Funding for public health initiatives that prioritize maternal care—such as community outreach programs, education about prenatal health, and support systems for new mothers—is essential. A robust public health infrastructure not only facilitates better tracking of maternal health outcomes but also fosters a more informed and responsive healthcare system.
Moreover, as public health funding faces cuts, there is a pressing need for advocacy to elevate maternal health on the national agenda. By mobilizing stakeholders—from healthcare providers to policymakers—we can push for necessary reforms that place maternal health at the forefront. A unified commitment to investing in maternal health infrastructure will ultimately lead to substantive changes in the way we approach pregnancy and postpartum care, significantly reducing pregnancy-related deaths and improving health outcomes across the board.
Innovations in Maternal Care: Moving Towards Comprehensive Solutions
Innovations in maternal care are vital for addressing the rising rates of pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S. Solutions such as telemedicine, improved training for healthcare providers, and community health worker programs can significantly enhance support for pregnant individuals throughout their journey. By leveraging technology and community resources, we can bridge the gaps in access to quality care, particularly in underserved populations. Implementing these innovative solutions can help ensure that all pregnant individuals receive the education, support, and resources they need to navigate their pregnancies safely.
Investing in training and education for healthcare professionals is equally important, as it cultivates a workforce that is well-equipped to address the diverse needs of pregnant individuals. Continuous professional development that prioritizes cultural competency and the management of chronic health conditions will further improve maternal care outcomes. By adopting a comprehensive approach to maternal health, we can make significant strides towards reducing preventable deaths and enhancing the overall healthcare experience for expecting mothers.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the key factors contributing to the high maternal mortality rate in the U.S. compared to other high-income countries?
The U.S. has one of the highest maternal mortality rates among high-income nations due to several factors, including a fragmented healthcare system, widespread health disparities, and inequitable access to care. Racial and ethnic biases also play a critical role, with certain groups, such as American Indian and Alaska Native women, facing disproportionately high pregnancy-related deaths. Chronic conditions like cardiovascular disease are becoming more prevalent in younger women, potentially contributing to these preventable deaths.
How many pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S. are considered preventable?
More than 80% of pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S. are classified as preventable, according to recent studies. This statistic underscores the urgent need for improved prenatal and postpartum care, particularly to address the disparities found across different states and racial groups.
What measures can be taken to reduce the rising trend of pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S.?
To combat the increasing rates of pregnancy-related deaths, experts suggest investing in public health infrastructure, enhancing healthcare access, and promoting policies that address systemic health disparities. Focusing on quality care during both prenatal and extended postpartum periods can help mitigate the factors contributing to preventable deaths.
What role do postpartum care and ‘late maternal deaths’ play in maternal mortality statistics?
Postpartum care is crucial in addressing maternal mortality, especially since nearly one-third of pregnancy-related deaths occur between 42 days and one year after pregnancy. The recognition of late maternal deaths highlights the importance of ongoing healthcare support beyond the immediate postpartum period and advocates for a shift to a more comprehensive view of maternal healthcare.
How does the COVID-19 pandemic impact the rates of pregnancy-related deaths?
The study indicates that the highest increase in pregnancy-related deaths occurred in 2021, possibly influenced by the COVID-19 pandemic. Although rates trended downward afterward, they remained higher in 2022 than in 2018, suggesting that pandemic-related challenges may have exacerbated existing disparities in maternal care.
What are the disparities in pregnancy-related death rates among different racial groups in the U.S.?
Significant disparities exist in pregnancy-related death rates among racial groups in the U.S. American Indian and Alaska Native women experience the highest rates at 106.3 deaths per 100,000 live births, compared to 27.6 for white women and 76.9 for non-Hispanic Black women. These stark differences highlight the need for targeted interventions to reduce inequities in maternal health outcomes.
Why is it important to examine maternal mortality beyond the traditional 42-day postpartum period?
Examining maternal mortality beyond the 42-day postpartum period is vital because many deaths occur during the first year after childbirth. Recognizing this extended timeframe allows for better designed healthcare systems that provide support to mothers throughout their recovery process, therefore leading to a reduction in pregnancy-related deaths.
How has the implementation of pregnancy checkboxes on death certificates improved tracking of pregnancy-related deaths?
The introduction of pregnancy checkboxes on death certificates across all 50 states has significantly improved the tracking of pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S. This system allows for more accurate data collection and analysis since 2018, providing insight into the trends and underlying causes of maternal mortality.
What is the significance of the research conducted on pregnancy-related deaths for future policy and healthcare practices?
The research highlights the need for continued investment in public health and emphasizes the importance of addressing disparities in maternal care. By understanding the trends and causes of pregnancy-related deaths, policymakers can implement targeted interventions to enhance health outcomes for mothers and reduce preventable deaths.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Increasing Rates of Pregnancy-related Deaths | The U.S. continues to lead high-income countries in maternal mortality, with a rise observed between 2018 and 2022. |
| Preventable Deaths | More than 80% of pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S. are preventable. |
| Disparities by Race | African American and Native American women face significantly higher maternal mortality rates compared to white women. |
| Change in Leading Cause of Death | Cardiovascular disease has surpassed hemorrhage as the leading cause of pregnancy-related deaths. |
| Late Maternal Deaths | Late maternal deaths (42 days to 1 year after pregnancy) account for nearly a third of all pregnancy-related deaths. |
| Need for Improved Healthcare Infrastructure | Innovative solutions and continued investment in public health infrastructure are necessary to reduce mortality rates. |
Summary
Pregnancy-related deaths in the United States are a critical health issue, reflecting a troubling trend of rising mortality rates among expectant mothers. A recent study indicates that the U.S. continues to have the highest rate of maternal mortality compared to other high-income nations, highlighting systemic healthcare challenges and significant racial disparities. The findings underscore the urgent need for comprehensive technological and policy interventions to decrease preventable deaths and improve maternal healthcare across the nation.