Is sugar addictive? This question has sparked significant debate among nutrition experts and researchers alike, especially because sugar is ubiquitous in our diets. Many people experience intense cravings for sweets, leading them to wonder if they are grappling with sugar addiction. While sugar does not meet all clinical criteria for addiction, its health effects and the compulsive behaviors it can engender suggest a complex relationship. As we explore the nuances of sugar addiction, it’s essential to understand both the psychological and physiological impacts of excessive added sugar intake on our overall health and dieting patterns.
The discussion surrounding the compulsive consumption of sweet substances often leads to questions about their potential for addiction. Many individuals find themselves battling strong urges for sugary foods, raising concerns about the implications of these cravings for their dietary habits. Scholars and health professionals frequently assess the relationship between our eating behaviors and the health consequences of excessive added sugar consumption. While sugar may not be classified as an addictive substance in the same vein as nicotine or alcohol, understanding its effects on the body can illuminate the reasons behind our attachment to sweet flavors. Therefore, examining the concept of sugar and its addictive properties becomes crucial for fostering healthier eating practices.
Understanding Sugar Addiction
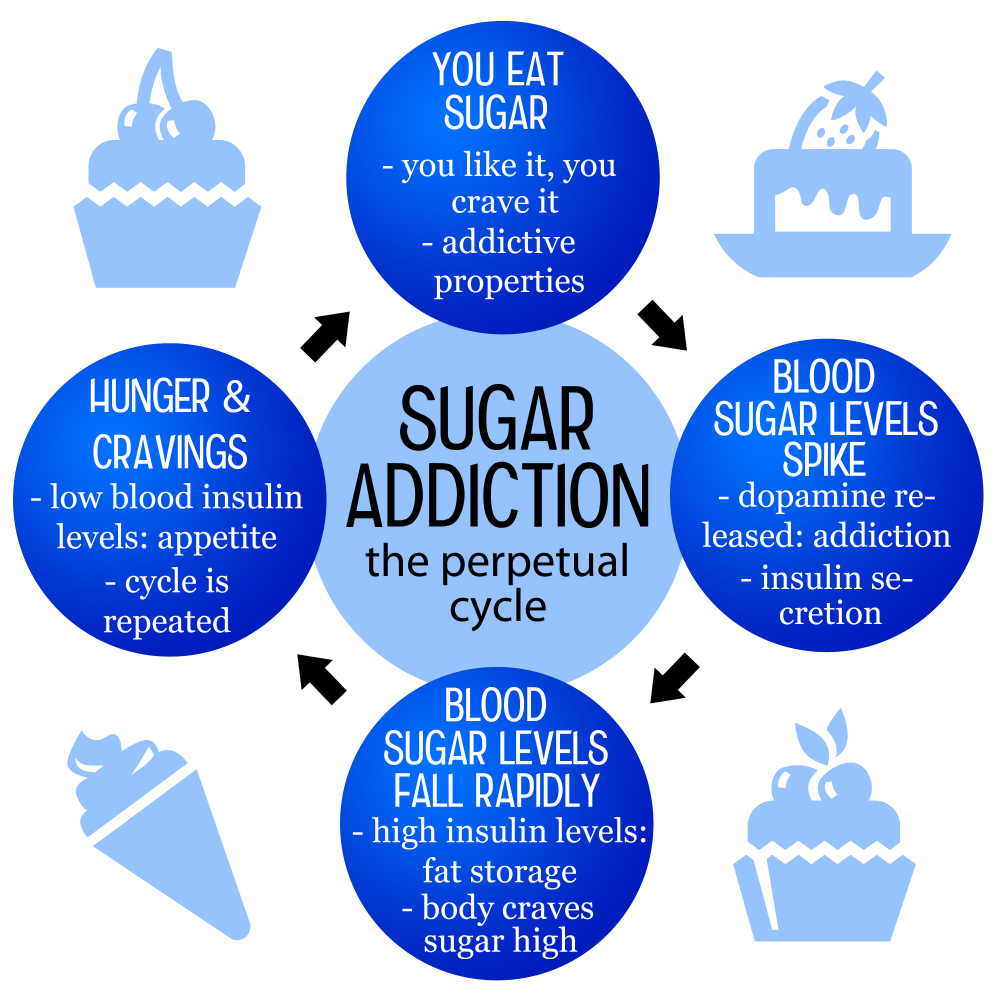
The question of whether sugar is addictive has sparked a significant debate in the nutritional science community. While substances like alcohol, nicotine, and opiates are categorized as addictive, sugar remains on the fringes of this classification despite evidence suggesting it can provoke cravings and compulsive behaviors. Nutrition researchers like Frank Hu emphasize that the widespread consumption of ultra-processed foods, laden with added sugars, can lead to increased cravings and habitual reliance on these sweetened products. In this sense, while sugar may not meet the strict clinical criteria for addiction, its potential to generate withdrawal-like symptoms when reduced can mirror addictive behaviors.
Cravings for sugar can be driven by both physical and psychological factors, making it essential to understand how these mechanisms work within our diet. The accessibility and palatability of sugary foods can lead to habitual overconsumption, causing individuals to develop a dependency on sweets for emotional or psychological comfort. This often results in an excessive intake of added sugar that surpasses the recommended daily limits set by health organizations, which suggest men should consume no more than 9 teaspoons and women no more than 6. Hence, while not officially classified as addictive, sugar does exhibit qualities that can resemble those of more recognized addictive substances.
The Health Effects of Excess Sugar Consumption
Excessive sugar intake has been linked to numerous adverse health effects, including obesity, type 2 diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases. The average American consumes approximately 20 teaspoons of added sugar a day, far exceeding the health recommendations. This surplus intake contributes to a range of metabolic disorders and elevates the risk of chronic diseases, prompting health experts to call for greater awareness regarding our sugar consumption habits. The frequent consumption of sugary beverages and snacks is particularly concerning, as these items are high in calories and low in nutritional value, leading to poor dietary choices and health complications.
Additionally, the psychological impacts of high sugar consumption cannot be overlooked. Studies suggest that excessive sugar can lead to mood swings and increased anxiety, creating a vicious cycle where individuals reach for more sweets to alleviate their discomfort. Understanding the health effects of sugar is imperative in making informed dietary choices. By gradually reducing added sugar intake rather than cutting it out completely, individuals can manage cravings more effectively and promote a healthier lifestyle. Moderation plays a crucial role, as optimal sugar consumption can enhance flavor in meals without significantly compromising health.
Navigating Diet and Sugar Intake Responsibly, Avoiding High Added Sugar Consumption
Incorporating sugar into a balanced diet does not have to be detrimental to health, but it requires careful consideration of how much sugar is consumed. Nutritionists recommend a mindful approach to diet that acknowledges the role of sugar in food while also limiting harmful added sugars found in processed snacks and sugary drinks. By reading food labels and understanding the sugar content in various products, individuals can make better choices that align with their health goals.
Moreover, finding natural sources of sugar, such as fruits and whole grains, can provide necessary sweetness without the health risks associated with added sugars. As experts suggest, gradually reducing added sugar in the diet rather than eliminating it entirely can prevent withdrawal-like symptoms and create a more sustainable lifestyle change. Additionally, pairing sugar consumption with fiber-rich foods can help mitigate its impact on blood sugar levels, leading to improved overall health outcomes.
Strategies to Curb Sugar Cravings
Managing sugar cravings involves understanding their triggers and finding effective strategies to combat them. Common techniques include ensuring the intake of balanced meals, which contain a good mix of proteins, fats, and complex carbohydrates. Such meals can stabilize blood sugar levels and reduce the likelihood of sugar cravings occurring between meals. Additionally, staying hydrated can often temper the desire for sugary snacks, as dehydration can sometimes be mistaken for hunger or cravings.
Mindful eating practices can be particularly beneficial in reducing cravings. Engaging with food fully by eliminating distractions during meals and savoring each bite can enhance satisfaction and prevent overconsumption of sugary items. Incorporating healthy snacks that fulfill a sweet craving – such as fruits or yogurt with natural sweeteners – can also help manage the urge to turn to less healthy options. These strategies are effective in developing a healthier relationship with sugar while still enjoying its flavor in moderation.
The Role of Sugar in Our Diet
Sugar, despite its notorious reputation, does play a critical role in our diets. Naturally occurring sugars found in fruits, vegetables, and dairy products contribute to essential nutrients that our bodies need. They provide energy and can stimulate satisfaction in meals, enhancing the overall eating experience. Understanding the differentiation between naturally occurring sugars and added sugars is vital, as the former typically come with various health benefits while the latter often lead to excess calorie consumption without nutritional value.
Moreover, the psychological comfort provided by sweetness is not to be understated. As mentioned by nutrition experts, sugar can enhance the flavor profiles of dishes and evoke feelings of pleasure, which is essential for maintaining a balanced and enjoyable diet. The key is to consume sugars in moderation, ensuring that they complement a diet rich in whole foods rather than dominate it. Thus, recognizing the role of sugar can allow for a healthier integration into daily meals.
Understanding the Psychological Aspects of Sugar Consumption
The psychological connection between sugar and mood is a significant aspect that invites further exploration. Many individuals turn to sugary foods for comfort during stressful times, revealing a link between emotional well-being and sugar intake. The pleasure derived from sugar consumption triggers the release of dopamine, creating a temporary mood boost that may contribute to habitual consumption patterns. Over time, this reliance can lead to the emergence of cravings whenever individuals experience stress or emotional upheaval.
Furthermore, addressing emotional eating linked to sugar consumption is crucial for breaking the cycle of addiction-like behaviors. Techniques such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) can help individuals understand their emotional triggers and develop alternative coping mechanisms. By learning to respond to stress with healthier strategies rather than seeking solace in sugary foods, individuals can effectively manage their cravings and contribute to a more balanced approach to diet and health.
How to Gradually Reduce Added Sugar Intake
Reducing added sugar intake is a journey that benefits from gradual changes rather than drastic cuts. Individuals are less likely to experience withdrawal symptoms when they decrease their sugar consumption slowly. For instance, one can start by replacing sugary beverages with healthier alternatives like water or herbal teas, and choosing snacks with lower sugar content. Substituting traditional desserts with fruit-based options can also satisfy sweet cravings without the adverse health effects of high added sugars.
Creating an environment that supports lower sugar intake can also enhance success. Keeping healthier food options visible and easily accessible while minimizing the presence of sugary snacks can foster better choices. Engaging in meal planning and cooking at home enables better control over ingredient selection, ultimately leading to reduced added sugar consumption and fostering a healthier lifestyle.
The Importance of Label Reading in Sugar Consumption
Label reading is an essential practice for anyone looking to manage their sugar intake effectively. Many packaged foods contain hidden added sugars, which may not be immediately obvious. By learning to interpret nutrition labels, individuals can make informed decisions that align with their dietary goals. Look for terms like ‘sucrose,’ ‘high fructose corn syrup,’ and ‘agave nectar,’ which often indicate added sugar content. Being aware of these terms helps consumers understand the nutritional value of their food.
Additionally, comparing sugar content among similar products can highlight better choices. This mindful comparison allows individuals to pick options with lower added sugars while still enjoying their favorite flavors. Being proactive about reading labels not only leads to healthier choices but can also help those struggling with sugar cravings to regain control over their dietary habits.
Balancing Sugar Intake with Healthful Eating Practices
Striking a balance between enjoying sugar and maintaining health is crucial for sustainable living. Rather than resigning to a strict ‘no sugar’ rule, embracing moderation can help individuals enjoy their favorite sweets without detriment to their health. This approach fosters a more positive relationship with food, as people learn to appreciate sweets as part of an overall healthy diet.
Incorporating healthful eating practices involves prioritizing whole foods while allowing for the occasional indulgence. For instance, enjoying a slice of cake during celebrations can coexist with a diet rich in vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. This balance can make it easier to satisfy cravings when they arise without compromising health.
The Impact of Sugary Beverages on Health
Sugary beverages are one of the top contributors to excessive sugar intake in the average diet. Drinks like soda, sweetened teas, and energy drinks can pack a significant amount of sugar with very minimal nutritional value, leading to an increased risk of obesity and metabolic disorders. Experts recommend limiting the intake of sugary drinks and opting for water or natural juices instead, as they can help control overall sugar consumption while improving hydration.
Furthermore, getting into the habit of reading beverage labels for sugar content is necessary for making healthier choices. Understanding how many teaspoons of sugar are in a typical bottle of soda is eye-opening for many and can promote a shift towards healthier alternatives. Making these informed choices can dramatically reduce daily sugar intake and contribute to long-term health benefits.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is sugar addictive like drugs and alcohol?
While sugar can create cravings and compulsive eating behaviors similar to addictive substances, it is not classified as an addictive drug like alcohol or nicotine. Sugar does affect the brain’s reward system, leading to a desire for more, but its classification as an addictive substance is still debated.
What are the health effects of sugar addiction?
Sugar addiction or excessive consumption of added sugars can lead to significant health issues, including obesity, type 2 diabetes, and heart disease. High added sugar intake is linked to increased cravings and can result in withdrawal-like symptoms if reduced abruptly.
How do sugar cravings develop in our diet?
Sugar cravings often develop from regular consumption of ultra-processed foods that contain high levels of added sugar. These foods are very palatable and easily accessible, which can establish a habit leading to increased cravings for sugar.
What is the recommended limit for added sugar intake?
The American Heart Association recommends that men should limit their added sugar intake to no more than 9 teaspoons per day, and women to no more than 6 teaspoons. Monitoring label information for sugar content can help manage this intake.
Can you eliminate all sugar from your diet?
Completely eliminating sugar from your diet is not feasible or healthy since sugar naturally occurs in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and dairy. A balanced approach is to reduce excessive added sugars while allowing for some natural sugars in moderation.
What strategies can help manage sugar cravings?
To manage sugar cravings, gradually reduce added sugar intake rather than going cold turkey. Look for healthier alternatives and read food labels to remain aware of hidden sugars. This can help lessen cravings over time.
What psychological effects do health issues from sugar have?
The psychological effects of excessive sugar consumption can include anxiety, mood swings, and withdrawal symptoms when sugar is reduced or eliminated. Awareness of one’s sugar intake and making gradual changes can mitigate these effects.
Why should I be aware of my sugar intake?
Being aware of your added sugar intake is crucial because excessive consumption can lead to various health problems, including increased cravings and negative health impacts, such as heart disease and diabetes. Monitoring sugar can promote a healthier diet.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Classification of Sugar | Sugar is not officially classified as addictive like alcohol or nicotine, but shows addictive-like effects in some behaviors. |
| Cravings and Withdrawal Symptoms | Cravings for sugary foods can lead to withdrawal-like symptoms such as headaches and anxiety when stopped suddenly. |
| Dietary Need | Sugar is essential in our diet as it naturally occurs in many healthy foods like fruits and dairy. |
| Average Sugar Consumption | Most Americans consume nearly 20 teaspoons of added sugar daily, exceeding recommendations of 9 teaspoons (men) and 6 teaspoons (women). |
| Recommendations for Sugar Intake | It is advisable to read food labels and gradually reduce added sugar to avoid negative health effects. |
| Balanced Approach | A moderate amount of sugar can enhance enjoyment in eating, suggesting a balanced approach rather than complete elimination. |
Summary
Is sugar addictive? This question reveals the nuances of our relationship with sugar and its impact on dietary habits. While sugar shows some addictive-like behavior, it is not classified as an addictive substance in the same way as drugs or alcohol. Understanding these distinctions is crucial, as we must consider how much added sugar we consume daily and how it can affect our health. Moderation and awareness in our sugar consumption are essential, allowing us to enjoy sweetness in our diets without detrimental health consequences.